Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Energy Efficiency, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California 93106, USA
2 Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo 152-8552, Japan
3 Materials Department, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California 93106, USA
4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California 93106, USA
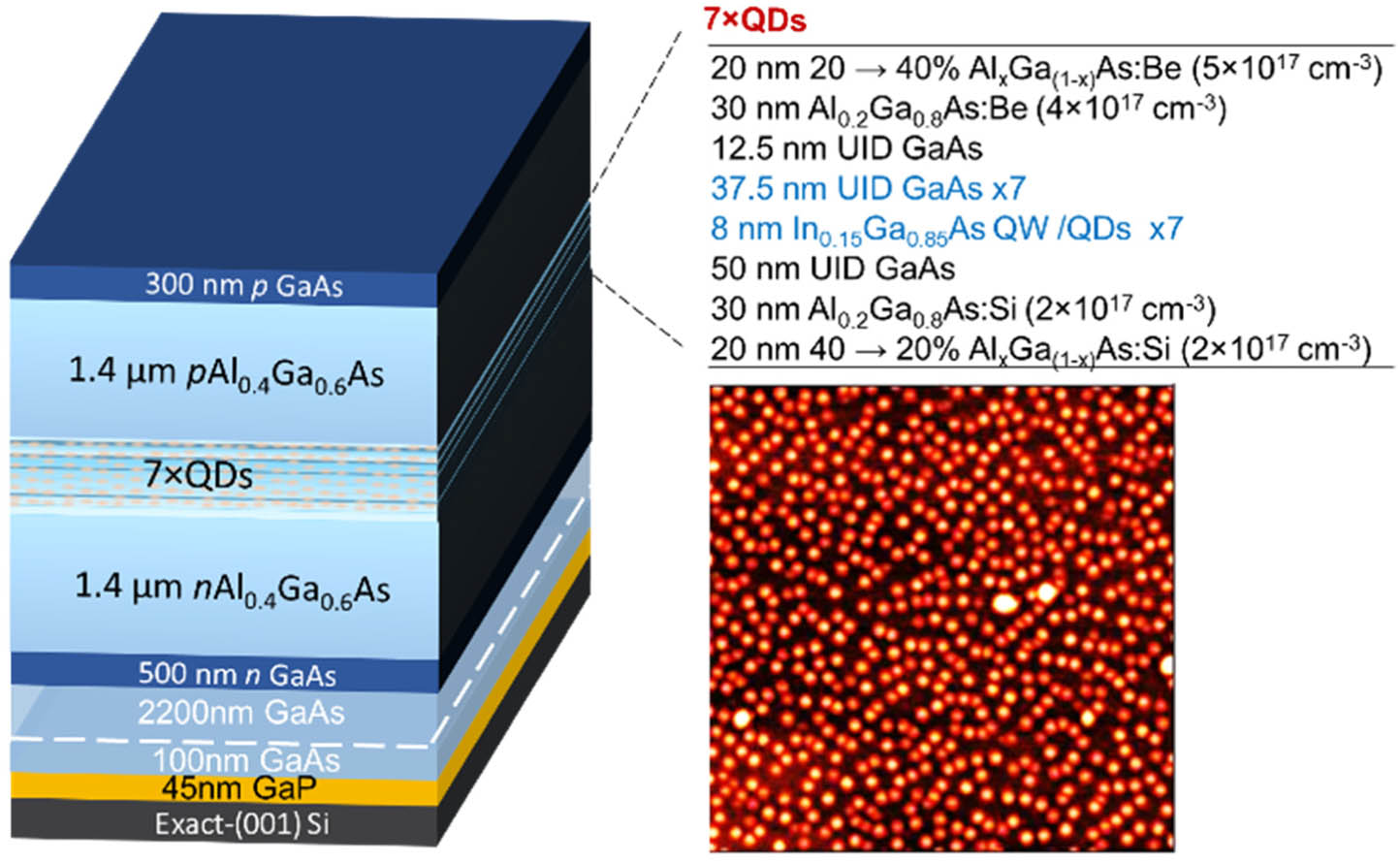
Microring lasers feature ultralow thresholds and inherent wavelength-division multiplexing functionalities, offering an attractive approach to miniaturizing photonics in a compact area. Here, we present static and dynamic properties of microring quantum dot lasers grown directly on exact (001) GaP/Si. Effectively, a single-mode operation was observed at 1.3 μm with modes at spectrally distant locations. High temperature stability with T0~103 K has been achieved with a low threshold of 3 mA for microrings with an outer ring radius of 15 μm and a ring waveguide width of 4 μm. Small signal modulation responses were measured for the first time for the microrings directly grown on silicon, and a 3 dB bandwidth of 6.5 GHz was achieved for a larger ring with an outer ring radius of 50 μm and a ring waveguide width of 4 μm. The directly modulated microring laser, monolithically integrated on a silicon substrate, can incur minimal real estate cost while offering full photonic functionality.
Quantum-well, -wire and -dot devices Semiconductor lasers Integrated optics materials Microcavities Photonics Research
2018, 6(8): 08000776
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and National Glycoengineering Research Center Shandong University, No. 44 Wenhuaxi Road Jinan 250012, P. R. China
2 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Shandong University, No. 27 Shandanan Road Jinan 250010, P. R. China
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. It is difficult to assign specific features under complicated system. So it is necessary to find the relevance between NIRS and target compound. For this purpose, the chondroitin sulfate (CS) ethanol precipitation process was selected as the research model, and 90 samples of 5 different batches were collected and the content of CS was determined by modified carbazole method. The relevance between NIRS and CS was studied throughout optical pathlength, pretreatment methods and variables selection methods. In conclusion, the first derivative with Savitzky–Golay (SG) smoothing was selected as the best pretreatment, and the best spectral region was selected using interval partial least squares (iPLS) method under 1mm optical cell. A multivariate calibration model was established using PLS algorithm for determining the content of CS, and the root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) is 3.934 g·L-1. This method will have great potential in process analytical technology in the future.
Chondroitin sulfate near infrared spectroscopy variable selection pathlength Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2014, 7(6): 1450022
1 哈尔滨师范大学生命科学与技术学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150025
2 黑龙江省农业科学院草业研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150086
用近红外漫反射光谱技术,结合偏最小二乘法(PLS),以152个来源不同的紫花苜蓿样品建立了粗蛋白和粗纤维含量的近红外定量分析校正模型。在近红外光谱范围内(950~1650nm)对紫花苜蓿样品采集光谱数据时,分别设置了粗磨样、细磨样两种样品的状态和1,2,5nm 三种光谱扫描间隔,对建立的模型进行准确性和重复性的验证,比较其优劣。结果显示:光谱扫描时样品为细磨样,光谱扫描间隔为2nm 时所建立的粗蛋白和粗纤维含量的校正模型最佳,其相关系数(R)分别是0.97和0.94,最佳因素数时的定标标准差(SECV)分别是0.42和0.78。所建近红外定量分析模型对独立检验集样品粗蛋白和粗纤维含量的预测值与化学值的相关系数(R)分别为0.96和0.92,预测标准差(SEP)分别为0.43和0.79。该研究结果表明:利用近红外漫反射光谱法测定紫花苜蓿内在主要品质性状是可行的,为紫花苜蓿粗蛋白和粗纤维含量的检验提供了新的方法模式。
近红外漫反射光谱 紫花苜蓿 含量 粗蛋白 粗纤维 Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy Content Alfalfa Crude protein Crude fiber Partial least squares(PLS) 光谱学与光谱分析
2009, 29(12): 3250





